Table Of Content

Since school days’ students perform scientific experiments that provide results that define and prove the laws and theorems in science. These experiments are laid on a strong foundation of experimental research designs. Laboratory experiments are conducted under controlled conditions, which allows for greater precision and accuracy. However, because laboratory conditions are not always representative of real-world conditions, the results of these experiments may not be generalizable to the population at large. This blog summarizes the concepts of cluster randomization, and the logistical and statistical considerations while designing a cluster randomized controlled trial. The major difference between experimental and quasi-experimental design is the random assignment of subjects to groups.
What are The Types of Experimental Research Design?
Adopting these ideas may improve your science and surely will enhance the communication of that science. These ideas will make experimental manuscripts easier to read and understand and, therefore, will allow them to become part of readers' clinical decision making. Community trials are also known as cluster‐randomized trials, involve groups of individuals with and without disease who are assigned to different intervention/experiment groups. Experimental research establishes a cause-effect relationship by testing a theory or hypothesis using experimental groups or control variables. In contrast, descriptive research describes a study or a topic by defining the variables under it and answering the questions related to the same. This website is using a security service to protect itself from online attacks.
Purpose of Experimental Design
This means that each experiment condition includes the same group of participants. To clarify the difference between study design and statistical analysis, to show the advantages of a properly written study design on article comprehension, and to encourage authors to correctly describe study designs. Overall, the purpose of experimental design is to provide a rigorous, systematic, and scientific method for testing hypotheses and establishing cause-and-effect relationships between variables.
Experimental design: Guide, steps, examples
Some examples of variables include age, sex, weight, height, health status, alive/dead, diseased/healthy, annual income, smoking yes/no, and treated/untreated. A confounding variable is related to both the supposed cause and the supposed effect of the study. It can be difficult to separate the true effect of the independent variable from the effect of the confounding variable. How precisely you measure your dependent variable also affects the kinds of statistical analysis you can use on your data. How you manipulate the independent variable can affect the experiment’s external validity – that is, the extent to which the results can be generalised and applied to the broader world.
An experimental design where treatments aren’t randomly assigned is called a quasi-experimental design. All variables which are not independent variables but could affect the results (DV) of the experiment. Appropriate study design statements also increase the accuracy of conclusions drawn from the study. The intertwining of study design and statistical analysis may have been caused (unintentionally) by R.A.
Experimental study on the influence of mental fatigue on risk decision-making of miners Scientific Reports - Nature.com
Experimental study on the influence of mental fatigue on risk decision-making of miners Scientific Reports.
Posted: Wed, 13 Jul 2022 07:00:00 GMT [source]
Cohort studies are study designs that compare two groups, such as the subjects with exposure/risk factor to the subjects without exposure/risk factor, for differences in incidence of outcome/disease. Most often, cohort study designs are used to study outcome(s) from a single exposure/risk factor. Thus, cohort studies can also be hypothesis testing studies and can infer and interpret a causal relationship between an exposure and a proposed outcome, but cannot establish it (Figure 4). The true experimental research design relies on statistical analysis to approve or disprove a hypothesis.
5 Sample size and replicates
When properly described in the written report of the experiment, it serves as a road map to readers,1 helping them negotiate the “Methods” section, and, thus, it improves the clarity of communication between authors and readers. Blinding is especially important in studies where subjective response are considered as outcomes. This is because certain responses can be modified based on the knowledge of the experiment group that they are in. However, certain treatments cannot be blinded such as surgeries or if the treatment group requires an assessment of the effect of intervention such as quitting smoking.
No Comments on An introduction to different types of study design
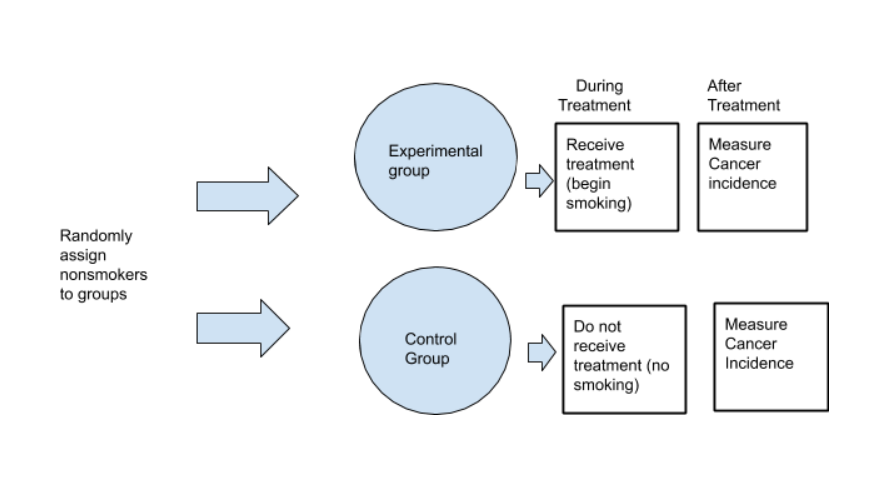
Now that you have a strong conceptual understanding of the system you are studying, you should be able to write a specific, testable hypothesis that addresses your research question. Use arrows to show the possible relationships between variables and include signs to show the expected direction of the relationships. Probably the most common way to design an experiment in psychology is to divide the participants into two groups, the experimental group and the control group, and then introduce a change to the experimental group, not the control group. Details of how they were measured are not given at this point in the manuscript but are explained later in the “Instruments” and “Procedures” subsections. Hence, while designing a research study, both the scientific validity and ethical aspects of the study will need to be thoroughly evaluated. By comparing their outcomes in biochemical tests, the researcher can confirm that the changes in the plants were due to the sunlight and not the other variables.
Subject Area
Counterbalancing (randomising or reversing the order of treatments among subjects) is often used in within-subjects designs to ensure that the order of treatment application doesn’t influence the results of the experiment. Sometimes this choice is made for you by your experimental system, but often you will need to decide, and this will affect how much you can infer from your results. Experimental design refers to how participants are allocated to different groups in an experiment. Types of design include repeated measures, independent groups, and matched pairs designs. The terms study design, experimental design, and research design are often thought to be synonymous and are sometimes used interchangeably in a single paper. Use the term that is preferred by the style manual of the journal for which you are writing.
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A FeaturePaper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook forfuture research directions and describes possible research applications. The issue of measurement bias arises due to unrecognizable differences in the evaluation process. Using the five steps to develop a research plan ensures you anticipate and eliminate external variables while answering life’s crucial questions. Researchers must ensure their experiments do not cause harm or discomfort to participants.
Have you ever interrupted your reading of the “Methods” to sketch out the variables in the margins of the paper as you attempt to understand how they all fit together? Or have you jumped back and forth from the early paragraphs of the “Methods” section to the “Statistics” section to try to understand which variables were collected and when? These efforts would be unnecessary if a road map at the beginning of the “Methods” section outlined how the independent variables were related, which dependent variables were measured, and when they were measured. When they were measured is especially important if the variables used in the statistical analysis were a subset of the measured variables or were computed from measured variables (such as change scores). A pre-experimental research study is a basic observational study that monitors independent variables’ effects.
Behavioral measures involve measuring participants’ behavior directly, such as through reaction time tasks or performance tests. Self-report measures involve asking participants to report their thoughts, feelings, or behaviors using questionnaires, surveys, or interviews. All rights are reserved, including those for text and data mining, AI training, and similar technologies. In an investigation of the effects of education on income, the factor being studied is education level (qualitative but ordinal). Babies do their own rudimentary experiments (such as putting objects in their mouths) to learn about the world around them, while older children and teens do experiments at school to learn more about science.
Thus, clinical trials can be used to evaluate new therapies, such as new drug or new indication, new drug combination, new surgical procedure or device, new dosing schedule or mode of administration, or a new prevention therapy. Hence, the case and control are matched on calendar time and length of follow‐up. When this study design is implemented, it is possible for the control that was selected early in the study to develop the disease and become a case in the latter part of the study. One of the limitations of case‐control studies is that they cannot estimate prevalence of a disease accurately as a proportion of cases and controls are studied at a time.
Case‐control studies are also prone to biases such as recall bias, as the subjects are providing information based on their memory. Hence, the subjects with disease are likely to remember the presence of risk factors compared to the subjects without disease. Vision is the main way for pilots to obtain information, and good visual ergonomics are an important support for ensuring aircraft flight safety. The range of illumination changes in the light environment of the aircraft cockpit is very wide, and research on the visual ergonomics of the cockpit needs to consider various extreme lighting conditions. The experimental results show that, except for head-up display, the accuracy of visual target interpretation tasks performed by other display devices under different brightness conditions remains at a high level. And as the brightness of the display device increases, the accuracy of interpretation gradually increases, and the reaction time gradually decreases.
It allows us to manipulate variables and observe the effects, which is crucial for understanding how different factors influence the outcome of a study. Experimental research design provides researchers with a controlled environment to conduct experiments that evaluate cause and effect. Under completely experimental conditions, researchers expose participants in two or more randomized groups to different stimuli. Developing a quality research plan means a researcher can accurately answer vital research questions with minimal error. As a result, definitive conclusions can influence the future of the independent variable.
This paper gives a brief overview of the common study types, and for those embarking on such studies you will need far more comprehensive, detailed sources of information. In studies that use experimental design, the independent variables are manipulated or controlled by researchers, which enables the testing of the cause-and-effect relationship between the independent and dependent variables. An experimental design can control many threats to internal validity by using random assignment of participants to different treatment/intervention and control/comparison groups. Therefore, it is considered one of the most statistically robust designs in quality-of-life and well-being research, as well as in... Thus, case‐control studies can also be hypothesis testing studies and therefore can suggest a causal relationship but cannot prove.

No comments:
Post a Comment